Beyond the blue links: Generative Engine Optimisation Guide
- Geethapriya Venugopal

- Jan 30
- 4 min read

The introduction of AI has fundamentally changed how users search for information. Users are no longer typing keywords and scanning blue links; now they are asking questions and expecting instant, contextual answers.
Large language models such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Claude, and Copilot now deliver direct responses, often without requiring users to visit traditional search engines. This shift is transforming how content is discovered and consumed.
As a result, digital marketing, especially Search Engine Optimisation, must evolve. Marketers need to adapt their strategies to align with changing user behaviour and AI-driven search experiences. This is where Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) comes into play.
In this guide, we’ll explore what Generative Engine Optimisation is, why it matters, and how you can increase your content’s visibility across generative AI platforms.
What is Generative Engine Optimisation?
Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) is the practice of optimising content so that generative AI systems can understand, trust, and reference it while generating answers to user prompts. Traditional SEO focuses on ranking top in search results, but GEO focuses on increasing your content for user prompts.
What is Generative Engine Optimisation?
According to Google, Gemini had 650 million users per month in November 2025. This is clear evidence that marketers should rework their strategy and focus more on GEO.
AI Visibility: GEO helps increase brand visibility on generative AI platforms by improving the likelihood that your content is referenced or mentioned in AI-generated answers.
Direct Answer: Users are shifting from browsing search results to interacting with AI tools that provide immediate answers. GEO ensures your content is structured in a way that AI systems can extract and present as part of those direct responses.
Evolution in organic search: According to a Gartner report, by 2026, traditional search engines will drop by 25%. This shift will impact organic traffic patterns and attribution models, pushing marketers to optimise not just for clicks, but for AI-driven visibility and influence.
Difference Between SEO and GEO

| SEO | GEO |
Concept | SEO focuses on ranking your webpage in the search engine results page (SERP) | GEO focuses on citing your webpage in generative AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini |
Content Approach | SEO focuses on keywords and search intent or user intent | GEO requires a specific content structure, authority, which needs to be AI-friendly. |
Visibility | Blue links | Conversational answer |
Metrics | Organic traffic, Keyword visibility, CTR, Ranking | Citation, Brand visibility, mentions |
Which LLM Engine needs GEO?
LLMs | Need |
ChatGPT | ChatGPT relies on a combination of licensed data, indexed content, and high-quality public information. GEO plays a role in making content clearer, more authoritative, and easier for the model to reference when generating responses. |
Perplexity | Actively references web pages and prioritises well-structured, authoritative content with clear sourcing. |
Google Gemini | Builds on Google’s index while generating AI answers, making SEO fundamentals and GEO optimisation closely connected. |
Microsoft copilot | Relies on Bing’s ecosystem and trusted web sources |
How to get cited in ChatGPT? GEO Strategy checklist?
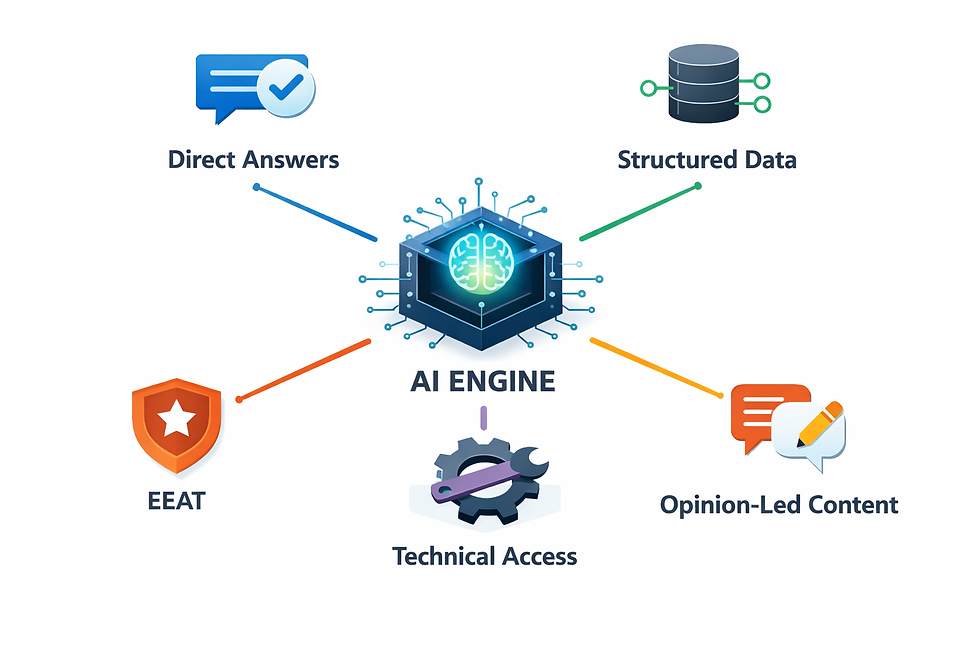
1. Direct Answer
To get cited in ChatGPT, the most important thing is content structure and writing. If your webpage ranks top in SERP doesn’t mean your content will be listed in LLMs because AI systems prioritise content with high information density and clear answers over verbose or generic explanations.
After your questionnaire header, write the direct answer in the first paragraph because AI will not read the entire blog; it will read only chunks of content.
Structure data or Schema markup
Structured data helps AI understand your content better. Using a schema like FAQ or Article makes it easier for AI tools to find clear answers. Simple headings, short paragraphs, and bullet points also help AI quickly pick the right information and use it in its responses.
EEAT
SEO has evolved into GEO and beyond, but authority remains constant. Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (EEAT) play a crucial role in GEO as well.
Generative AI systems are trained to prioritise high-quality signals, which include expert insights, original experience, credible sources, and relevant industry statistics or benchmarks.
Technical Access
Allowing AI crawlers such as GPTBot or CCbot through your robots.txt file improves content accessibility. However, accessibility alone does not guarantee citations.
Files like llms.txt can act as a guidance layer for AI systems, highlighting important pages and content structure. Ultimately, citations depend on content quality, relevance, authority, and clarity, not crawling permissions alone.
The End of Generic TOFU Content
The approach to top-of-funnel (TOFU) content is changing. AI systems are increasingly capable of answering basic definitional queries such as “What is CRM?” without referencing individual websites.
Modern TOFU content should focus on unique perspectives, first-hand experience, opinions, and differentiated insights rather than generic explanations.
Middle-of-funnel (MOFU) and bottom-of-funnel (BOFU) content, such as comparisons, use cases, and decision-stage content, remain largely unchanged and continue to play a critical role in conversions.
Wrap-up: Beyond Blue Links, The Future Is Generative
Search is no longer limited to ten blue links. With large language models delivering instant, contextual answers, brands can’t rely on traditional SEO alone. That’s where Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) comes in.
GEO shifts the focus from ranking pages to earning citations, mentions, and visibility inside AI-generated answers. By creating well-structured, intent-matched content backed by expertise, data, and trust signals, businesses can position themselves as reliable sources for LLMs like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
In short, SEO brings traffic, and GEO builds presence in the AI era. Winning brands will invest in both.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) is the practice of optimising content so that AI models and large language models cite, reference, or use it while generating answers to user prompts.
2. How is GEO different from traditional SEO?
SEO focuses on ranking webpages on search engine result pages, while GEO focuses on getting your content referenced inside AI-generated answers across tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
3. Does GEO replace SEO?
No. GEO does not replace SEO. SEO helps search engines find and rank your content, while GEO helps AI systems trust and reuse your content as a source.
4. How do AI models decide which content to cite?
AI models prioritize content that is:
Clearly structured
Directly answers questions
Backed by expertise and data
Written with authority and trust signals (EEAT)
5. Does structured data help with GEO?
Yes. Structured data like FAQ, How-To, and Article schema helps AI systems understand content context, improving citation and extraction accuracy.



Comments